- Anatomy
- Conditions
- Procedures
Stress Fractures of the Hip
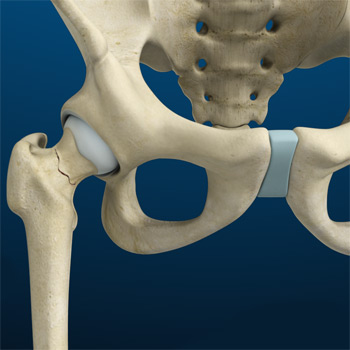
Stress fractures of the hip are a break in the upper part of the thigh bone (femur) that fits into the socket of the hip joint. It can occur in any part of the hip, however, it mostly occurs just below the ball of the ball-and-socket hip joint called the femoral neck.
Hip Injury

The hip joint is one of the most important and flexible joints in the human body which allows us to walk, run, bend and perform physical activities. It is a ball (femoral head) and socket joint formed between the hip bone and femur (thighbone). It is surrounded by strong muscles and tough ligaments that prevent its dislocation.
Hip Pain

The hip joint is one of the most important and flexible joints in the human body which allows us to walk, run, bend and perform physical activities. It is a ball (femoral head) and socket joint formed between the hip bone and femur (thighbone). It is surrounded by strong muscles and tough ligaments that prevent its dislocation.
Snapping Hip Syndrome

Snapping hip syndrome is a condition in which you hear or feel a snapping sound in the hip when you swing your legs, run, walk or get up from a chair. The sound can be experienced in the back, front or side of the hip.
Hip Bursitis

Hip bursitis is a painful condition caused by the inflammation of a bursa in the hip. Bursae are fluid-filled sacs present in the joints between bone and soft tissue to reduce friction and provide cushioning during movement.
Avascular Necrosis

Avascular necrosis, also called osteonecrosis, is a condition in which bone death occurs because of inadequate blood supply to it. Lack of blood flow may occur when there is a fracture in the bone or a joint dislocation that may damage nearby blood vessels. Hip joint is most commonly affected; however, the knee and shoulder may also be involved.
Hip Dislocation

The hip joint is a “ball and socket” joint. The “ball” is the head of the femur or thighbone, and the “socket” is the cup-shaped acetabulum. The joint is surrounded by muscles, ligaments, and tendons that support and hold the bones of the joint in place. Hip dislocation occurs when the head of the femur moves out of the socket. The femoral head can dislocate either backward (posterior dislocation) or forward (anterior dislocation).
Subtrochanteric Hip Fracture

A hip fracture is a break that occurs near the hip in the upper part of the femur or thighbone. The thighbone has two bony processes on the upper part - the greater and lesser trochanters. The lesser trochanter projects from the base of the femoral neck on the back of the thighbone. Hip fractures can occur either due to a break in the femoral neck, in the area between the greater and lesser trochanter or below the lesser trochanter.
Osteoarthritis of the Hip

Osteoarthritis, also called degenerative joint disease, is the most common form of arthritis. It occurs most often in the elderly. This disease affects the tissue covering the ends of bones in a joint called cartilage.
Inflammatory Arthritis of the Hip

The inflammation of the joints is referred to as arthritis. Inflammation arises when the smooth lining called cartilage at the ends of bones wears away. In some cases, the inflammation is caused when the lining of the joint becomes inflamed as part of an underlying systemic disease. These conditions are referred to as inflammatory arthritis.
Partial Hamstring Tears

The hamstring is a group of three muscles known as semimembranosus, semitendinosus, and biceps femoris that run along the back of the thigh from the hip to the knee and help you extend your hip and bend your knee. Partial hamstring tears occur when one or more of these muscles get overstretched, strained, or pulled. They are common in dancers and athletes of all sorts including runners and those who play football, soccer, basketball, tennis, etc.
Hamstring Injuries

The hamstring is a group of three muscles that run along the back of the thigh from the hip to the knee. Hamstring injuries occur when these muscles are strained or pulled. They are common in dancers and athletes of all sorts including runners and those who play football, soccer, basketball, tennis, etc.
Hip Adductor Injuries

Hip adductors are the group of muscles on the inner side of your thigh that enable adduction or the ability to bring the thighs together. A hip adductor injury is also called a groin strain or groin tear and involves any of the adductor muscles. These injuries are common among athletes and those who play hockey, football, soccer, basketball, tennis, baseball, etc.
Gluteal Strain

A gluteal strain is a condition characterized by a partial or complete tear of the gluteus muscles, also known as the buttocks. The gluteus muscles are a group of strong muscles present at the back of the pelvis. These muscles help with the movement and stabilization of the hip joint.
Hip Bone Cysts

Hip bone cysts, also referred to as subchondral bone cysts, are fluid-filled sacs or spaces that form in one or both of the bones that make up a hip joint. The cysts develop just below the cartilage (tough spongy tissue) that covers the bone near the joint. The sacs typically consist of hyaluronic acid, a constituent found in synovial fluid, which is a thick substance that lubricates joints, enabling the bones to slide past one another without friction.
Hip Ligament Injuries

Injuries to the hip ligaments are commonly called a hip sprain and can range from minor tears of the ligaments to more serious injuries involving the hip muscles, tendons or bone. The hip joint is a ball and socket joint; the ball being the head of the femur (thigh bone) and the socket is the acetabulum of the pelvis. Tendons, muscles, and ligaments hold the joint in place.
Femoral Subchondral Cysts

Femoral subchondral cysts are fluid-filled sacs or spaces that form in the femur (thighbone) side of the hip joint. Subchondral refers to the layer of bone just below the cartilage in a joint. The suffix ‘chondral’ means cartilage, while the prefix ‘sub’ means below. Subchondral bone acts as a shock absorber in a weight-bearing joint such as a hip joint.
Acetabular Fracture

An acetabular fracture is a break in the acetabulum (ball-and-socket portion) of the hip joint. It usually occurs during high-energy injuries.
Gluteus Tendon Tear

The gluteal muscles (situated in the buttocks) are necessary for the stability and movement of the hip joints. The tendons of two gluteal muscles (gluteus medius and gluteal minimus) are attached at the outer hip region and are often called the “rotator cuff of the hip.” These tendons may be subject to injury or tearing due to various reasons.
Pelvic Fractures

A pelvic fracture is a condition that occurs due to the breakage of the pelvic bone. It may cause damage to the internal organs, nerves and blood vessels associated with the pelvic region. The pelvic bone is a circular arrangement of bones connected with the help of strong ligaments to the lowermost region of the spine called the sacrum.
Femoroacetabular Impingement

Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) is a condition characterized by excessive friction in the hip joint from the presence of bony irregularities. These cause pain and decreased range of hip motion. The femoral head and acetabulum rub against each other, causing damage and pain to the hip joint.
Hip Fracture

The hip joint is a “ball and socket” joint. The “ball” is the head of the femur or thighbone, and the “socket” is the cup-shaped acetabulum. The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular surface that allows pain-free movement in the joint. A hip fracture is a break that occurs near the hip in the upper part of the femur or thighbone.
Gluteus Medius Tear

A gluteus medius tear is the partial or complete rupture of the gluteus medius muscle due to severe muscle strain. Gluteus medius tears often occur at the tendinous attachment to the greater trochanter of the femur bone.
Hip Labral Tear

A hip labral tear is an injury to the labrum, the cartilage that surrounds the outside rim of your hip joint socket.
Hip Instability

Injury or damage to these structures can lead to a condition called hip instability when the joint becomes unstable.
Hip Abductor Tears

Hip abductors are a major group of muscles found in the buttocks. It includes the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fascia lata muscles.
Hip Synovitis

Hip synovitis, also called transient hip synovitis or toxic synovitis, is a condition characterized by inflammation of the synovial tissues that surround the hip joint. It is the most common cause for sudden hip pain that occurs in young children between the age of 2 and 9. It affects boys more commonly than girls and is most of the time limited to only one side of the hip.
Developmental Dysplasia
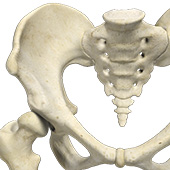
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) or hip dysplasia is a condition that is seen in infants and young children because of developmental problems in the hip joint. The femur (thighbone) partially or completely slips out of the hip socket leading to dislocation at the hip joint. It is most common in the first-born baby with a family history of the disorder.
Legg-Calve-Perthes-Disease

Legg-Calve-Perthes disease (LCPD) or Perthes disease is a disorder of the hip that affects children, usually between the ages of 4 and 10. It usually involves one hip, although it can occur on both sides in some children. It occurs more commonly in boys than girls.
Hip Tendonitis

Tendons are strong connective tissue structures that connect muscle to bone. Hip tendonitis is a condition associated with degeneration of the hip tendons. This condition is mainly caused due to strain on the tendons which may occur due to overuse or biomechanical problems.
Hip Pointer

The hip joint consists of the femur (thighbone) and pelvic bone, which is made up of the fusion of three bones – the ischium, pubis, and ilium. The femur has two boney prominences close to the hip joint – the greater and lesser trochanters. Hip pointer is an injury or bruise to the iliac crest (curved upper border of the ilium) or greater trochanter, or the surrounding muscles or tissues.
Femur Fracture

The femur or thigh bone is the longest and strongest bone in the body, connecting the hip to the knee. A femur fracture is a break in the femur. The distal femur is the lower part of the thigh bone which flares out like an upside-down funnel and its lower end is covered by a smooth, slippery articular cartilage that protects and cushions the bone during movement.
Spastic Hip Dysplasia

Spastic hip dysplasia is a hip disorder in which the acetabulum, the hip socket, doesn't cover the femoral head properly. As a result, the patient suffers from abnormal hip development which typically includes either partial or complete hip dislocation. Spastic hip dysplasia is caused by spasticity induced by cerebral palsy, a neuromuscular disorder that impairs muscle movement and coordination.
Hip Osteonecrosis

Hip osteonecrosis occurs due to disruption of the blood supply to the highest part of the thigh bone (femoral head). Due to lack of nourishment, the bone tissue of the femoral head dies and gradually collapses, which may further lead to degeneration of the underlying cartilage.
